Book a dental appointment
Severe periodontitis
Severe periodontitis affects 5–15% of population in developed countries. This disease initiates acute immunological responses of the body to specific bacteria that cause inflammatory response with which the body tries to protect itself. To put it simply, the bone is lost around bacterial growths to avoid them from spreading to the bone tissue and then to the bloodstream and other tissues. Although a similar protective mechanism of the body is at work in case of mild-to-moderate forms of periodontitis, it progresses at a much slower pace.
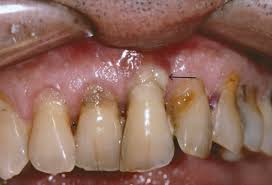
Severe periodontitis
Severe periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis
Aggressive periodontitis is a severe chronic inflammation that damages the tooth’s attachment apparatus and can cause teeth to start moving. This often leads to tooth loss later in life. Mild to moderate forms of the disease are common but do not cause significant problems. Aggressive periodontitis, which is difficult to treat, is rarely seen but does occur.
Aggressive periodontitis is an especially severe and rapidly progressive disease (0.5–1% of the population in developed countries). This disease may affect patients at any age and begins often in prepuberty. The disease is characterised by family aggregation and rapid loss of attachment tissues. The extent of the disease is not often consistent with the amount of plaque on the teeth. If left undiagnosed and untreated, the patients may lose teeth already before the age of 20.
Loose teeth can be partially fixed with different types of splints or they are removed and if possible, replaced with implanted teeth or dentures. General strengthening procedures are also recommended, and smoking and other harmful habits must be given up. The treatment plans possible in our clinic are explained in more detail by a corresponding specialist – dentist-periodontist. For more information about our periodontists, please visit our staff page.
Modern treatments can stop the disease to some extent, but gum tissues cannot be completely restored.
- Diagnosis
- Objective of periodontitis treatment
- Non-surgical treatment of periodontitis
- Surgical treatment of periodontitis
- Surgical extension of a crown
- Mucogingival surgery
- Side effects of treatment
- When diagnosis and treatment are late
Read more about our other dental treatment services here.
Read more about oral health here.
